SQL Joining
The attributes in the same domain in the joined tables do not need to have same names.
- INNER JOIN:如果表中有至少一个匹配,则返回行
- LEFT JOIN:即使右表中没有匹配,也从左表返回所有的行
- RIGHT JOIN:即使左表中没有匹配,也从右表返回所有的行
- FULL JOIN:只要其中一个表中存在匹配,则返回行
SELF JOIN:用于将表连接到自己,就好像该表是两个表一样,临时重命名了SQL语句中的至少一个表CARTESIAN JOINorCROSS JOIN:从两个或多个连接表返回记录集的笛卡儿积

JOIN and INNER JOIN#
On the basis of the column which is explicitly specified in the ON clause. The resulting table will contain all the attributes from both the tables including common/duplicated columns. INNER JOIN 与 JOIN 是相同的。
INNER JOIN or JOIN return the same result. JOIN is more useful when we specified conditions.(Difference between Natural join and Inner Join in SQL)
The following diagram illustrates the INNER JOIN clause:
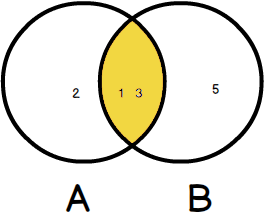
This logic is applied if you join more than 2 tables.
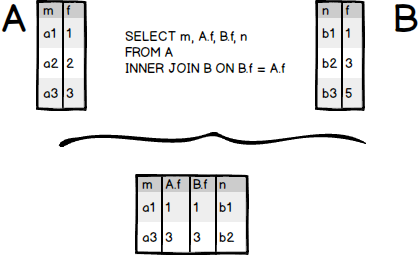
NATURAL JOIN#
It creates an implicit join clause based on the common columns in the two tables being joined. It is based on same attribute name and datatypes. The resulting table will contain all the attributes of both the table but keep only one copy of each common column.(no NO nor HAVING conditions can be specified)
If there are some tuples having different values of common attributes, these tuples will be discarded after joining together.
A NATURAL JOIN can be an INNER join, a LEFT OUTER join, or a RIGHT OUTER join. The default is INNER join.
SQLite automatically finds the attributes to merge on.
If the SELECT statement in which the NATURAL JOIN operation appears has an asterisk (*) in the select list, the asterisk will be expanded to the following list of columns (in this order):
- All the common columns
- Every column in the first (left) table that is not a common column
- Every column in the second (right) table that is not a common column
An asterisk qualified by a table name (for example, COUNTRIES.*) will be expanded to every column of that table that is not a common column.
LEFT JOIN#
Combines two relations on specific attributes.
The statement returns a result set that includes:
- Rows in table A (left table) that have corresponding rows in table B.
- Rows in the table A table and the rows in the table B filled with
NULLvalues in case the row from table A does not have any corresponding rows in table B.(can have different names)
In other words, all rows in table A are included in the result set whether there are matching rows in table B or not.
In case you have a WHERE clause in the statement, the search_condition in the WHERE clause is applied after the matching of the LEFT JOIN clause completes.
See the following illustration of the LEFT JOIN clause between the A and B tables.
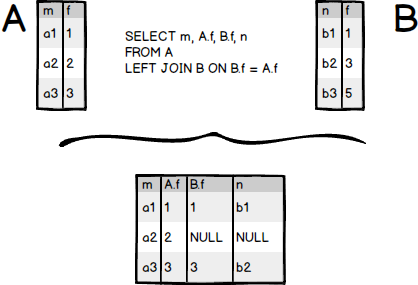
The following Venn Diagram illustrates the LEFT JOIN clause.
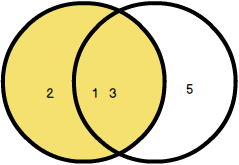
It is noted that LEFT OUTER JOIN is the same as LEFT JOIN
Examples:#
Retrieve the product names and product colors that have been ordered by ALEX or CAROL:
